We present a fast method for physically-based animation of fluids on adaptive, unstructured meshes. Our algorithm is capable of correctly handling large-scale fluid forces, as well as their interaction with elastic objects. Our adaptive mesh representation can resolve boundary conditions accurately while maintaining a high level of efficiency.
| Scene | # of cells | secs/frame | ||
| Fluid | Solid | Total | ||
| Bridge | 31k | 0.6 | 5.72 | 6.36 |
| Skyscrapers | 9k | 0.15 | 4.77 | 4.92 |
| Space station | 25k | 0.46 | 14.53 | 14.99 |
We have implemented our method and tested it on several demonstrative scenes; skyscrapers buffeted by swirling winds, an iconic bridge rocked by gusts of air, and a space station deforming under a flow of fluid-like particles.
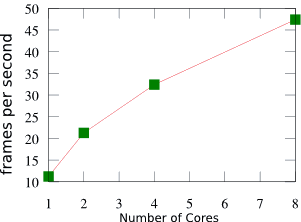
Our method is capable of exploiting the parallelism of modern multi-core processors. We have parallelized our RDS fluid solver using OpenMP; this figure demonstrates the near-linear scaling we have achieved. This measurement was performed on an SGI Altix machine.